Have you ever thought about the differences between Hajj and Umrah?
Both pilgrimages are sacred journeys that hold immense significance in Islam. While they involve traveling to Mecca and performing rituals, they serve distinct purposes and follow unique guidelines.
Understanding these differences is crucial for Muslims to approach each pilgrimage with the right intentions and practices.
Let’s dive in!
1. Definition
Hajj, the annual Muslim pilgrimage, holds significance as one of the five foundational pillars of the Islamic faith. The rituals performed during Hajj were firmly established by the teachings and practices of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH).
The Quran attributes these rites to Prophet Ibrahim (AS), who left his wife and son in Mecca's barren desert. Islamic beliefs emphasize that performing Hajj with faith reflects submission to Allah and earns divine merit.
Umrah, a pilgrimage to Mecca, differs as it can be performed at any time of the year. Muslims call it the ‘minor pilgrimage,’ which purifies pilgrims and absolves them of past sins. Umrah is highly recommended in Islam as it represents devotion, worship, and acknowledgment of Allah's infinite grace.
2. Obligation
The main difference between Hajj and Umrah is their legal status under Islamic teachings and practices. Performing Hajj is a mandatory obligation for those who meet the physical and financial conditions.
This duty is backed by the Quranic verse from Surah Al-Imran:
"The Hajj pilgrimage takes place during well-known months. Whoever has made Hajj obligatory upon themselves by entering the state of ihram, must refrain from sexual relations, misbehavior, and disputing during Hajj. And whatever good you do – Allah knows it."
The legal status of Umrah, however, varies according to different scholarly opinions across Islamic schools of thought. Maliki and most Hanafi scholars view Umrah as a highly recommended Sunnah, not a mandatory act.
This understanding is supported by a hadith where Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) clarified the voluntary nature of Umrah:
"No. But if you perform Umrah, it is better."
(Sunan al-Tirmidhi)
Another narration highlights the distinction, stating:
"Hajj is Jihad, and Umrah is voluntary."
(Sunan Ibn Majah)
Conversely, some Shafi'i and Hanbali scholars consider Umrah necessary once in a lifetime, citing the Quranic directive:
"And complete the Hajj and Umrah for Allah."
(Surah Al-Baqarah: 196)
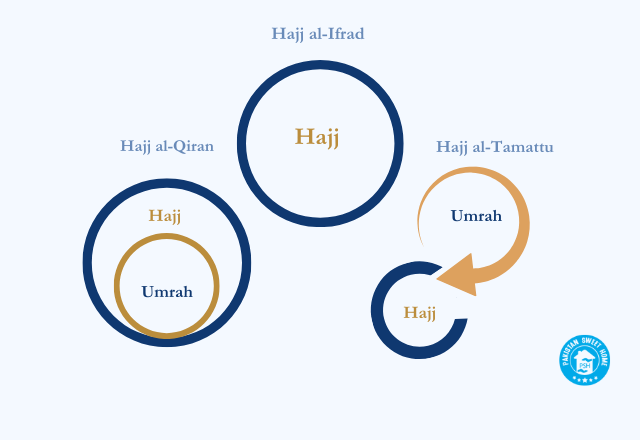
Hajj and Umrah differ in their requirements. Each pilgrimage has specific actions that are obligatory (Fard), recommended (Sunnah), and necessary (Wajib).
Duty of Hajj
- Fard:
o Ihram
o Waqf at Arafat
o Tawaf al-Ziyarah - Wajib:
o Sa'i
o Waqf at Muzdalifah
o Jamarat
o Halaq or Qasas
o Tawaf al-Wada
o Qurbani (sacrificing an animal) - Sunnah:
o Tawaf al-Qudum
o Staying in Mina on the 8th of Dhul-Hijjah (Tarwiyah)
o Cleansing the body before assuming Ihram and applying scent before wearing the Ihram garment
o Staying on the Tashriq days in Mina
o Staying in Muzdalifah on the night of Eid al-Adha
o Staying briefly in Muhassab or Abtah on the return from Mina
Duty of Umrah
- Fard:
o Ihram
o Tawaf - Wajib:
o Sa'i
o Halaq or Qasas - Sunnah:
o Pray 2 rakahs of Nafl Salah, reciting Surah al-Kafirun in the first rakah and Surah al-Ikhlas in the second
o Performing Ramal (brisk walking)
o Touching the Rukn-e-Yamani and kissing or touching the Black Stone
3. Timing of Performance
Hajj is restricted to specific months and performed only once annually. The prescribed months for Hajj, according to Islamic tradition, are Shawwal, Dhul-Qi'dah, and the first ten days of Dhul-Hijjah.
This is emphasized in the hadith:
"The months of Hajj are Shawwal, Dhul-Qi'dah, and ten days of Dhul-Hijjah."
(Sahih al-Bukhari: 1572)
Hajj rituals begin on the 1st of Shawwal (day of Eid al-Fitr) and end on the 13th of Dhul al-Hijjah. Arafah takes place on the 9th of Dhul al-Hijjah.
In contrast, Umrah has no fixed timing and can be performed throughout the year without restrictions. This flexibility makes it more accessible for Muslims to complete outside the Hajj season.
4. Duration
Hajj takes longer to complete due to the greater number of rituals involved.
Hajj rituals typically span about one week. However, the journey often extends to approximately 20-30 days for regular Hajj pilgrims. This extended period allows pilgrims to perform Umrah and visit other holy sites. They can also participate in Arbain at the Prophet’s Mosque.
Umrah, in contrast, is shorter and can be completed in a brief timeframe. Most Umrah pilgrims stay in Mecca for 9-12 days, depending on their chosen Umrah package.
5. Rituals
While Hajj and Umrah share certain rituals, they also have significant differences.
Here’s a look at the key rituals for each pilgrimage:
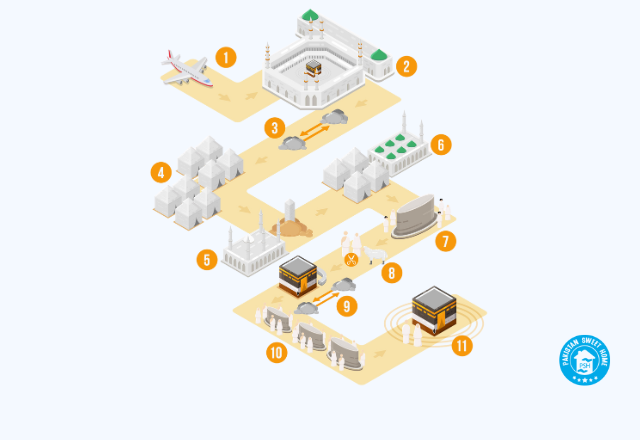
Hajj Rituals
Hajj includes several important rituals, such as:
- Ihram: Pilgrims enter the state of Ihram by wearing the prescribed white garments, which are seamless for men. They must also observe specific restrictions during this sacred state.
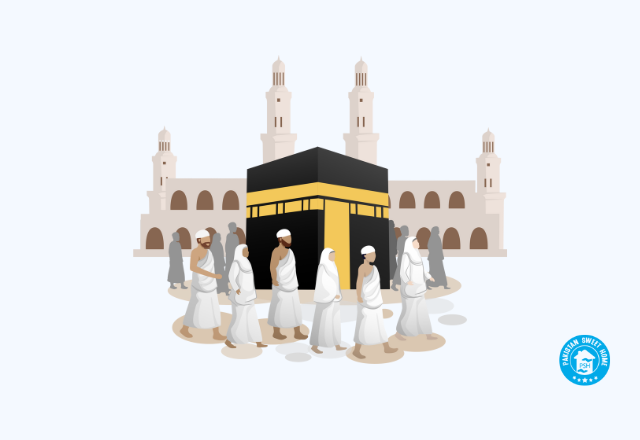
- Tawaf: Pilgrims perform Tawaf by walking around the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise motion.
- Sa'i: After Tawaf, pilgrims walk seven times between the hills of Safa and Marwah, reenacting the actions of Hajar.
- Wuquf in Arafah: On the 9th day of Dhul-Hijjah, pilgrims gather in Arafah. There, they engage in prayer and seek Allah’s forgiveness.
- Muzdalifah: After sunset, pilgrims travel to Muzdalifah to spend the night and gather pebbles for the upcoming ritual.
- Stoning of the Devil: Pilgrims stone three pillars in Mina, symbolizing the rejection of evil temptations.
- Sacrifice (Qurbani): A sacrificial animal is offered in remembrance of Prophet Ibrahim. It honors his willingness to sacrifice his son for Allah.
- Halq or Taqseer: Pilgrims either shave their heads or trim their hair to signify the completion of the Hajj rituals.
- Tawaf al-Ifadah: Pilgrims return to the Kaaba to perform Tawaf al-Ifadah, symbolizing the completion of their Hajj.
- Sa'i of Hajj: After Tawaf, pilgrims perform Sa'i between Safa and Marwah once again, completing the pilgrimage.
Umrah Rituals
Umrah includes following rituals.
- Ihram, a sacred state before the journey.
- Tawaf, where pilgrims walk around the Kaaba in an anti-clockwise motion, symbolizing devotion and unity.
- Sa’i, is a ritual walk between Safa and Marwah, representing the daily struggles of life.
- Tahallul involves breaking the state of Ihram by shaving the head after completing Umrah.
6. Location
Another difference between Hajj and Umrah lies in the locations of their rituals. Hajj encompasses multiple sites, including Arafah, Muzdalifah, and Mina. While Umrah is confined to Mecca, many pilgrims also visit Medina as part of their journey.
7. Cost
A key distinction between Hajj and Umrah is the difference in cost. Hajj offers various packages, including Hajj Plus, regular Hajj, and individual Hajj. Among these, Hajj Plus and individual Hajj packages are considerably more expensive than the regular Hajj option.
In comparison, Umrah is significantly less expensive, making it a more accessible pilgrimage for many Muslims.
8. Organizers
The Ministry of Religious Affairs and Interfaith Harmony (MoRA&IH) in Pakistan plays a vital role in organizing both Hajj and Umrah.
For Hajj, the MoRA&IH’s Hajj Wing collaborates with various stakeholders, including the Pakistani and Saudi governments. It also works with banks, airlines, and scholars to ensure smooth arrangements for pilgrims.
Additionally, the ministry also oversees and facilitates Umrah, making it more accessible and organized for Pakistani pilgrims.
Similarities Between Hajj and Umrah
While Hajj and Umrah differ in several aspects, they also share notable similarities.
Here are some key similarities between Hajj and Umrah:
- Both pilgrimages take place in Mecca, Saudi Arabia
- The main purpose of both Hajj and Umrah is to worship Allah and seek His blessings
- Pilgrims are required to enter the state of Ihram for both rituals
- Certain rituals, such as the Tawaf of the Kaaba, Sa’i, and shaving or trimming of the head, are common to both
- Pilgrims for both Hajj and Umrah must adhere to similar restrictions, including avoiding sinful actions and prohibited behaviors
Mandatory Requirements for Hajj and Umrah
Both Hajj and Umrah have essential prerequisites that must be met before undertaking these pilgrimages.
There are seven key requirements for performing these rituals:
1. Faith in Islam
Hajj is the fifth pillar of Islam, completing the other foundational pillars. If a non-Muslim attempts to perform Hajj, their worship is invalid. This rule also applies to Umrah.
2. Reaching Puberty
The second requirement is reaching puberty or adulthood. Individuals who have not yet reached puberty can perform these rituals. However, their worship does not fully meet the valid conditions.
3. Mental and Physical Health
Pilgrims must be mentally and physically healthy. Those with mental disabilities, memory loss, or insanity are not obligated to perform Hajj or Umrah.
4. Freedom
Pilgrims must be free, meaning they should not be under any form of bondage or servitude. Although slavery is no longer common, performing Hajj and Umrah is not important for slaves or indentured servants. This exemption applies to those who are Muslims.
5. Capability
Pilgrims must have the ability to undertake the journey, as stated in the Quran:
"Hajj is an obligation for those who can make the journey to the Kaaba, as commanded by Allah."
(Surah Al-Imran: 97)
This includes both financial and physical capability. Financially, pilgrims should afford the costs without neglecting other essential needs. Physically, they must be able to perform the necessary rituals.
6. Availability of Transportation
Access to reliable transportation is mandatory for Hajj and Umrah. If pilgrims do not own a vehicle, they must be able to finance transportation for the journey. This is necessary to ensure smooth travel between pilgrimage sites.
7. Safe Journey
Safety is crucial, meaning pilgrims should not face significant dangers or hardships during the pilgrimage. This includes the safety of oneself, one's soul, and possessions. Specifically, women performing Hajj or Umrah must have a mahram or travel with trusted female companions.
Tips for Preparing for Hajj and Umrah
After understanding the differences between Hajj and Umrah and the mandatory requirements for both.
Here are some tips to help you prepare:
1. Focus on Physical Health
Hajj and Umrah require good physical stamina. Schedule a comprehensive health check-up and consult a doctor about your health status. Enhance your physical readiness by exercising regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, and ensuring adequate rest.
2. Plan Your Budget
The expenses associated with Hajj and Umrah can be substantial. Engage in detailed financial planning by estimating costs related to travel, accommodation, visas, and personal needs. Start saving early and allocate funds consistently to cover these expenses.
3. Organize Necessary Documents
Collect important documents like your passport, visa, ID cards, and confirmation of Hajj/Umrah registration. Ensure that all documents are accurate and valid before you leave.
4. Familiarize Yourself with Saudi Arabian Regulations
Understand the rules and cultural norms of Saudi Arabia to prevent any violations. Learn about the specific rituals of Hajj and Umrah, along with the appropriate attire. Understand local customs to ensure a respectful and smooth pilgrimage experience.
In conclusion, Hajj and Umrah are two unique Islamic pilgrimages, each holding its own importance, timing, and set of rituals. Hajj is mandatory and occurs within a specific period, while Umrah is optional and can be performed at any time, except during the Hajj period.
Both pilgrimages offer immense spiritual rewards, allowing Muslims to deepen their faith, seek forgiveness, and draw closer to Allah. Regardless of the difference between Hajj and Umrah, both journeys share commonalities and provide a profound spiritual experience.
Muslims should be aware of the essential requirements for both Umrah and Hajj. It’s also important to take helpful tips before embarking on the journey.
Each orphanage center of Pakistan Sweet Home is built with care to provide a secure and loving environment for orphans. These centers operate across Pakistan and offer everything from food and shelter to sports and education. The centers are a second home where children are raised with values and hope.
Reserve Your Seat in Jannah!

info@pakistansweethome.org.pk
(051) 4865856
+92 335 1118477